This methodology detects genomic deletions and duplications involving this locus including the seven most common types of α-Thalassemia. DNA analysis of the α-globin region HBA1HBA2 OMIM 141800141850 16pter-16p133 is performed by targeting 28 different sequences using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification MLPA.
 Frontiers Gene Mutation Spectrum Of Thalassemia Among Children In Yunnan Province Pediatrics
Frontiers Gene Mutation Spectrum Of Thalassemia Among Children In Yunnan Province Pediatrics
The beta-thalassemia DNA test detects the most common HBB genetic mutations known to cause beta-thalassemia.
Thalassemia dna test. Simple mouth swab DNA test. DNA analysis is also the only reliable way of diagnosing carriers who have only one of four alpha genes deleted or mutated and who have normal haemoglobin and red cells in the basic blood tests. This test analyses DNA extracted from whole blood for the major mutations found in the HBB gene which represent the mutation spectrum found in Indian thalassemic subjects- IVS 1-5 GC IVS 1-1 GT 619 bp deletion Codon 15 GA Codon 30 GA FS 89 G FS 4142 CTTT.
DNA testing is the only way to determine silent alpha thalassemia trait and the related hemoglobin trait called hemoglobin Constant Spring. Genetic testing DNA testing of the HBB gene can be used to diagnose beta-thalassemia. In the setting of reproductive counselling identification of a two-gene cis deletion in both prospective parents indicates they are at risk of having a fetus with hemoglobin Bart hydrops fetalis which is almost always fatal before birth.
Because of the enormous diversity in clinical severity of thalassemia patients complete DNA testing prior to commencement of treatment is required to determine prognosis appropriate therapy and family counseling. For beta thalassemia the hemoglobin beta gene HBB may be analyzed or sequenced to confirm the presence of thalassemia-causing mutations. Beta β thalassemias are a group of inherited blood disorders.
DNA analysis on chorionic villi is the approach for prenatal diagnosis and the methods are the same used for mutations detection according to the laboratory facilities and expertise. Thalassemia served as a disease model to develop strategies for NIPT of monogenic traits. INTRODUCTION Thalassemia syndromes are a heterogeneous group of hemoglobin disorders due to a decreased or absent production of normal globin chains.
Carrier testing for at-risk relatives and prenatal testing are possible if the disease-causing mutations in the family are known. 60-80 million people around the world carry a β-thalassemia mutation making it the most common autosomal recessive disorder in the world. Beta-thalassemia is diagnosed using genetic testing and blood tests.
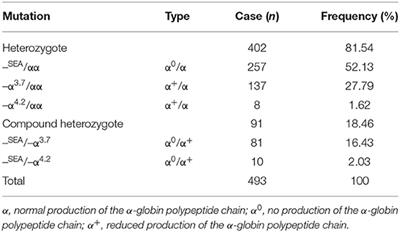
More than 95 of recognized α-thalassemia involves deletion of one or both α-globin genes from chromosome 16p133. They are the most common recessive diseases worldwide. Alpha-globin genotype was determined by PCR-based method in 526 adult subjects with reduced mean corpuscular volume MCV and mean corpuscular hemoglobin.
Definitive diagnosis and family counseling should be done in conjunction with a thalassemia center. The Genetic Testing Registry GTR is a centralized online resource for information about genetic tests. In particular in alpha thalassaemia it is important to know if a person with alpha thalassaemia trait has two mutated genes on one chromosome or one on each chromosome.
One approach focuses on the detection or exclusion of paternally inherited fetal mutations that are absent from the mothers genome. In this paper we report our experience in the identification of the alpha-thalassemia carrier state using polymerase chain reaction PCR-based methods and the feasibility and simplification of screening for thalassemia using this approach. DNA testing may also be necessary in order to allow for the option of prenatal testing.
DNA testing is not routinely done but can be used to help diagnose thalassemia and to determine carrier status if indicated. 7 mL whole blood 10 mL amniotic fluid or 20 mg CVS. DNA TESTING PRIOR TO TREATMENT.
Clinical test for alpha Thalassemia offered by Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory. Defects in the HBB gene cause β-thalassemia. DNA analysis provides definitive diagnosis of alpha-thalassemia trait and determines whether a patient has a one-gene deletion or a two-gene cis deletion.
Yes genetic testing is available for HBB HBA1 and HBA2 the genes known to cause thalassemia. Whole blood amniotic fluid chorionic villus sample CVS Submission of maternal blood is required for fetal testing Volume. Beta Thalassemia Mutation Analysis.
Prenatal testing may be considered if both parents are carriers of mutations known to cause beta-thalassemia. DNA testing is an important tool in establishing an accurate diagnosis of thalassaemia.